Virtualization
Suzhou Metalogic Information Technology Co.,Ltd 2018-11-08 14:14:26 Author:SystemMaster
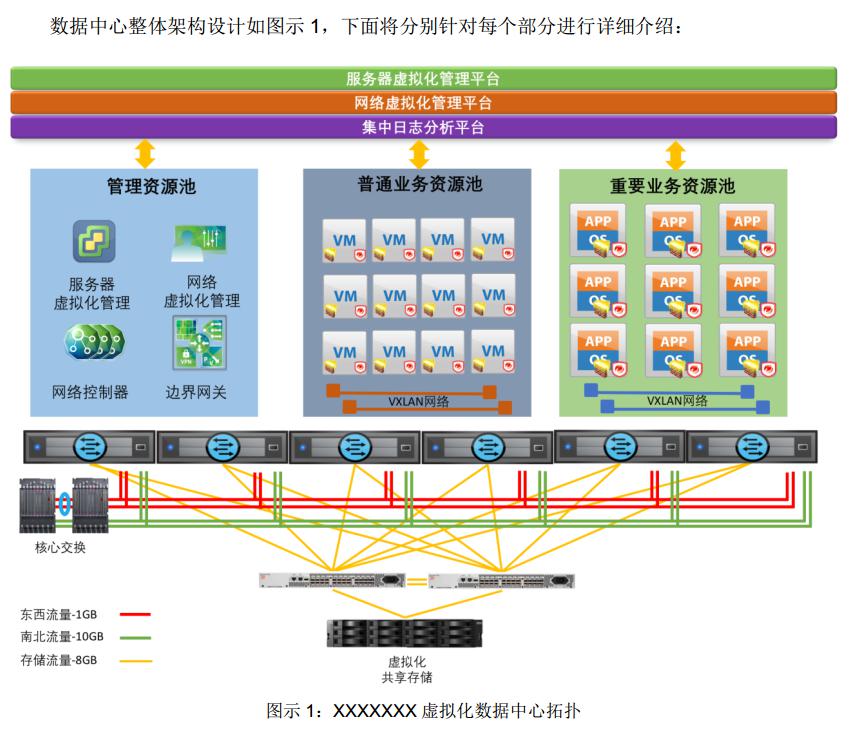
1、Server Performance and Capacity Planning
In the early stages of virtualization, there was a virtual machine capacity plan that was how many virtual machines could be placed on a physical server. In fact, this is a comprehensive problem, that is, consider the CPU, memory, and disk (capacity and performance) of the host, and also consider the resources required by the running virtual machine,when used in practice, the system always has at least 30 % or more surplus capacity, It is not possible to use more than 80 % of the resources on a host to be close to 100 %. Otherwise, once these values are reached, the system response will be relatively slow.
When estimating the capacity of virtualization, in the case of CPUs only, physical CPUs and virtual CPUs can be planned at a ratio of 1:4 to 1:10 or higher. For example, a physical host has four 8-core CPUs. If there is enough memory and storage, According to the ratio of 1:5, it can be virtual 4 × 8 × 5 = 160 vCPU, assuming that each virtual machine needs 2 vCPU, you can create 80 virtual machines. In the project where virtualization is actually implemented, most virtual machines do not have very high CPU requirements. Even if four or more CPUs are assigned to the virtual machine, the CPU usage of the virtual machine is actually only 10 % or less. The physical host CPU resources consumed at this time are less than 0.5
In virtualization projects, memory usage is the largest and the highest requirement. In actual use, it is often found that the memory of a physical host will be close to 80 % or even 90 %. Because, on the same physical host, the number of planned virtual machines is large, and the memory allocated by each virtual machine is larger(always more than the actual memory used by the virtual machine), it will result in a reduction in the available memory of the host. When configuring memory for a physical host, consider how many virtual machines are to be run on the host and how much memory these virtual machines require. In general, each virtual machine requires 1GB to 4GB or more of memory, and a portion of memory is reserved for VMware ESXi. In general, four 8-core CPUs are configured, and it is generally necessary to configure 96GB or even higher memory; In a host with two 6-core CPUs, 32 to 64GB of memory is usually configured.
2、Statistics and calculation of existing server capacity
If you want to migrate an existing physical server to a virtual machine, you can create a statistical table that includes the CPU model, number, CPU utilization, existing memory and memory utilization, existing hard disk number, size, RAID, and usage of the existing physical server. Then based on these calculations, the calculation method is:Actual CPU resources = CPU frequency × CPU number × CPU usage
Actual memory resource = the server memory × memory usage rate
Actual hard disk space = hard disk capacity-remaining space
Assuming that after calculation, 91.1944 Gz CPU resources have been used. Taking the CPU frequency 3.0 Hz CPU as an example, 30 cores(100 % load) are required, but the CPU load rate in the overall project is considered to be 60 % to 75 %. And other overhead, such as management, requires at least 40 CPU cores. If you configure 4 6-core servers, you need about 4 physical hosts.
As for memory, assume that 182GB has been used after calculation, plus management and surplus, calculated at 360GB, 96GB to 128GB per server.
3、Server selection for server virtualization
In the process of virtualization, existing servers can be used if they can meet requirements for virtualization. If the existing server does not fully meet the requirements, you can partially use the existing server and then purchase the new server.
If new servers are procured, more products are available for selection. If the unit computer room is stored in the cabinet, the priority is to purchase the rack server. The principle of server procurement is:
(1)If the 2U server can meet the requirements, the 2U server will be used. Under normal circumstances, the 2U server will have maximum support, 2 CPUs, and 1 CPU. At this time, 2 CPUs will be configured.
If the 2U server can not meet the requirements, use the 4U server instead. Under normal circumstances, the 4U server supports up to 4 CPUs and is equipped with 2 CPUs. When purchasing a server, it is advisable to configure 4 CPUs for the server. If there is no limit to the number of servers, purchasing twice as many 2U servers will save more money than purchasing 4U servers, and most of the performance will also meet the requirements.
(2)CPU: When selecting a CPU, it is advisable to select a 6-core or 8-core Intel series CPU. A 10-core or more core CPU is more expensive and is not recommended. Of course, the unit has higher performance and space requirements for the CPU. exception.
(3) Memory: When configuring the server, it is possible to configure more memory for the server. In virtualization projects, memory is more important than CPU. Under normal circumstances, two 6-core 2U servers are configured with 64GB of memory, and four 6-core or 8-core 4U servers are configured with 128GB or more of memory.
(4) Network Card: When selecting a server, consider the number of network cards of the server. At least, the server must be configured with a two-interface gigabit network card. The four-port gigabit network card is recommended.
(5) Power supply: It is possible to configure two power sources. Under normal circumstances, the 2U server selects 2 450W power supplies to meet the demand, and the 4U server selects 2 750W power supplies to meet the demand.
(6)Hard disk: If the virtual machine is stored in the server's local storage, instead of network storage, it is advisable to configure six hard disks for RAID5 or eight hard disks for RAID50 for the server. Due to the limited number of hard disk slots on the server, it is not possible to select a small hard disk. At present, the cost-effective is 600GB SAS hard disk, the 2.5-inch SAS hard disk speed is 10,000 rpm, the 3.5-inch SAS hard disk speed is 15,000 rpm, and the 2.5-inch hard disk is selected higher IOPS.
As for the server brand, you can choose Huawei, IBM, HP, or Dell. When there is a high demand for server space, you can configure blade servers, such as Huawei Tech E 6000 server, 8U space, which can configure up to 10 blade servers. Each server can be equipped with 2 CPUs, 2 SAS hard drives, 12 memory slots, and dual-port network cards.
4、Options for storage devices
In the virtualization project, it is recommended to use storage devices instead of server local hard disks. When configuring shared storage devices, only virtual machines can be stored in storage to quickly implement and use HA, FT, vMotion and other technologies. When using VMware vSphere to implement the virtualization project, a recommended approach is to install VMware ESXi on the server's local hard disk. This local hard disk can be a solid-state hard disk(5.2 to 10GB can be), it also can be an SD card(configuration 8GB can be), and it even can be a 1GB USB disk. If the server does not have a local hard disk configured, it can also divide 8 to 16GB of partitions for the server from storage for startup.
When choosing a storage device, consider the storage capacity, disk performance, number of interfaces, and bandwidth of the interface required in the entire virtualization system. For capacity, the capacity of the entire storage design should be more than twice the actual capacity of us,.For example, the entire data center already uses 1TB of disk space(all self-added space), then when designing storage, design at least 2TB of storage space(after configuring RAID, not without configuring RAID, all disks Add space).
Another important parameter in storage design is IOPS (Incut / Outcut Operations Per Second), which is the number of read-write(I/O) operations per second. This is mostly used for databases and other occasions to measure the performance of random access. The storage side's IOPS performance is different from the host's IO. IOPS refers to how many times per second the host can receive access. A host's IO requires multiple access to the storage to complete. For example, whenever the host writes a minimum data block, it must go through three steps: "Send a write request, write data, and receive a write confirmation." It is accessed by three storage terminals. , each disk system has an upper limit of IOPS. If the actual IOPS in the designed storage system exceeds the upper limit of the disk group, the system response will slow down and affect the performance of the system. In simple terms, the IOPS for 15,000 rpm disks is 150, the IOPS for 10,000 RPM disks is 100, and the IOPS for ordinary SATA hard disks is about 70-80. Under normal circumstances, when doing desktop virtualization, the IOPS of each virtual machine can be designed as 3 to 5; Ordinary virtual server IOPS can be planned to be 15 to 30(according to the actual situation). When designing a system that runs 100 virtual machines at the same time, IOPS is planned to be at least 2,000. If you use a 10,000-turn SAS disk, you need at least 20 disks. Of course, this is only a simple calculation. There are many factors that need to be taken into account in real implementation.
When planning storage, consider the number of interfaces stored and the speed of the interface. In general, in planning a system with 4 hosts and 1 storage, it is more appropriate to use a storage server with 2 interfaces and 4 SAS interfaces. If there are more hosts, or if the host requires redundant interfaces, you can consider storage with FC interfaces and use fiber optic switches to connect storage to the server.
5、Network and Switch Selection
In a virtualized environment, each physical server generally has a higher network card density, and it is common for virtualization hosts to have 6, 8 or more network interface cards (NICs). Conversely, there are only two or four NICs that are not virtualized, which becomes a problem in the data center. Because the edge or distributed switch is placed in the rack to simplify the network wiring and then connect to the network core, in this solution, a typical 48-port switch can only handle 4 to 8 virtual hosts, in order to completely fill the rack, more edge or distributed switches are needed.
In a virtualized environment, when multiple workloads are integrated into these hosts, network traffic increases depending on the number of workload running on the host, and network utilization is no longer as low as it used to be on each physical server.
In order to adjust the network traffic from the integrated workload increase, it may be necessary to increase the number of uplinks from the edge or distributed switches to the network core. At this time, the backplate bandwidth and uplink lines of the switches reach higher requirements.
When doing dynamic migration between virtual machines, or migrating virtual machines from one store to another, in order to reduce the time of migration, it does not affect the key business and will occupy a large amount of network resources during the migration.In addition, although the number of concurrent migrations can be reduced at the time of migration, in some applications, multiple virtual machines may be migrated at the same time, which requires higher bandwidth and performance of switches.
In addition, virtualization has reduced some of the visibility of the network layer in the data center, network engineers do not have visibility in the virtual switch and can not easily determine which physical NIC corresponds to which virtual switch, this is the most important information in troubleshooting. In order to reduce the failure rate, the allocation of redundant business boards and redundant power supplies for switches should also be considered. At the same time, in the near future, higher switches should be configured.
In most cases, the physical host is configured with a 4-port gigabit network card, and for redundancy, it may be that every two network cards are bound together for load balancing and failover.
For the virtualization environment of small and medium-sized enterprises, the deployment of Huawei S5700 series gigabytes of switches for virtualization systems can meet most of the needs.
Huawei S5700 series is divided into 24 ports and 48 ports. If you need higher network performance, you can choose Huawei S9300 series switches. In virtualization planning, virtual machines in physical hosts only need to be in the same network segment (or in two other limited network segments), and when the performance requirements are not high but the price is sensitive, Huawei's S1700 series can be selected as general switch.
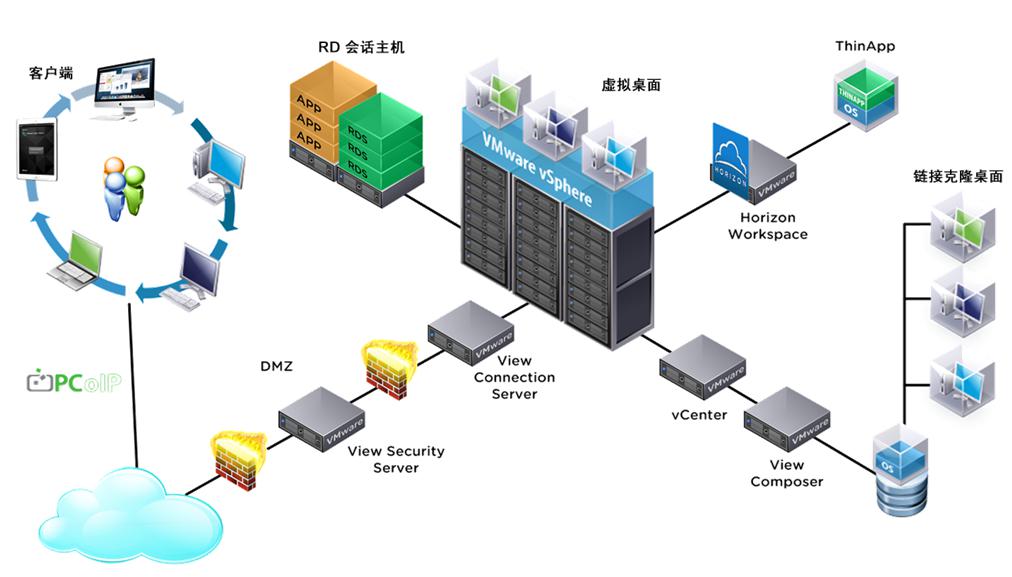
Virtualization
Desktop virtualization and desktop cloud to help clients meet challenges
The new desktop virtualization technology solves the above problems well and can logically separate the physical devices, operating systems, applications, and data used by users, but all this is completely transparent to end users, and this technical feature allows companies to truly achieve a balance between IT centralized control and user freedom. VMware's desktop virtualization and desktop cloud solutions can help users meet these challenges in the following ways.
The delivery of virtual or managed desktops and applications through a single platform simplifies management and reduces costs. Easy for users to license and deliver Windows and Linux resources across multiple data centers on a large scale. Simplify operating system migration and effectively isolate applications to prevent compatibility problems between the Windows platform and ThinApp.
A single digital workspace allows end-users easy access to virtual desktops and released applications, including RDS hosting applications and Citrix XenApp. Through Blast Performance, different devices, locations, media, and network connections can provide a realistic and versatile user experience for end users.
With the help of instant cloning technology, App Volumes and user environment management, the rapid deployment of a fully functional, personalized and digital workspace based on the economic advantages of non-persistent desktops. Deliver and update the application immediately upon end-user login. Easily monitor performance, establish active alarm mechanisms, and repair infrastructure, desktops, and applications to improve user experience and increase user satisfaction.
Smart strategies to streamline access processes
Streamline end user access and simplify authentication across all desktop and application services with a truly single-point login and role-based and sophisticated contextual strategy (associated with user, device, and location information). With the help of simplified network links, automated smart systems, and full-range threat prevention services from data centers to devices, the virtual infrastructure is protected by multiple layers.
Data Center Construction Based on Software Definition
Horizon is supported by data centers defined by VMware software, which can improve security, simplify operations, and shorten value implementation time. With VMware vSphere, Horizon's customers can enjoy proven scalability, high availability, and best performance. VMware NSX for Horizon uses security strategies that follow the dynamic movement of end users across infrastructure, devices, and locations to make VDI network connections fast and simple. With VMware Virtual SAN, customers can reduce start-up costs and use a large number of pre-configured devices that have been optimized for Horizon, including Virtual SAN ready node devices and EVO SDDC infrastructure.